Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically within the fallopian tube, presenting significant risks if not promptly addressed. This blog explores the symptoms, causes, and treatment modalities available for managing ectopic pregnancies.
What is Ectopic Pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy is a condition where the fertilized egg attaches and grows outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. This abnormal development can lead to severe complications if left untreated. Throughout this discussion, we will explore the diverse array of symptoms, root causes, and various treatment options available for this condition.
Symptoms
The symptoms associated with ectopic pregnancy can vary widely among individuals. Common indications include vaginal bleeding, pelvic discomfort, nausea, vomiting, sharp abdominal pains, unilateral bodily discomfort, dizziness, fatigue, and discomfort in the shoulder, neck, or rectum. It is essential to seek immediate medical attention if one experiences intense pain accompanied by heavy vaginal bleeding, light headedness, fainting, shoulder pain, or severe abdominal discomfort, particularly on one side.
Causes
Several factors contribute to the heightened risk of ectopic pregnancy, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), smoking habits, advanced maternal age (above 35 years), sexually transmitted infections (STIs), pelvic surgery-induced scarring, previous history of ectopic pregnancy, and the application of fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
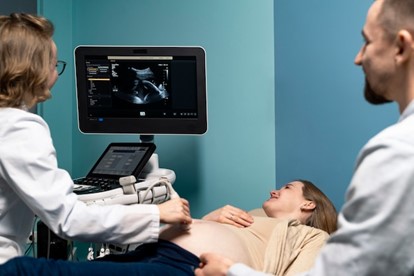
Ectopic Pregnancy Ultrasound
In diagnosing ectopic pregnancy, physicians often conduct pelvic examinations and administer blood tests to detect human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels—a pregnancy hormone. Furthermore, ultrasound imaging allows for a detailed visualization of the uterus and fallopian tubes to pinpoint the exact location of the ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
Due to the inability of ectopic pregnancies to be sustained in the uterus, prompt treatment is imperative. Primary treatment methods encompass medicinal intervention and surgical procedures:
- Medication: Methotrexate stands as the predominant pharmacological treatment for ectopic pregnancy. It halts cell growth, leading to the cessation of pregnancy. The residual embryo is naturally absorbed by the body over a span of 4 to 6 weeks.
- Surgery: Emergency surgical intervention becomes necessary if the ectopic pregnancy has ruptured a fallopian tube. Surgical procedures may also be recommended in cases where rupture has not occurred, with laparoscopy being a favored method. This minimally invasive procedure employs a slender, illuminated camera inserted through tiny abdominal incisions under general aesthesia to remove the ectopic pregnancy.
Ectopic Pregnancy Recovery
Recovery from ectopic pregnancy varies among individuals and can encompass several weeks of recuperation. Continuous monitoring and follow-up appointments are crucial post-treatment to ensure proper healing and to address any residual concerns.
Ectopic pregnancy necessitates swift medical intervention due to its potential for serious complications. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options enables individuals to promptly seek medical assistance and receive appropriate care. By fostering awareness and knowledge, we empower individuals to effectively manage ectopic pregnancies and mitigate associated risks, thereby promoting optimal reproductive health and well-being.