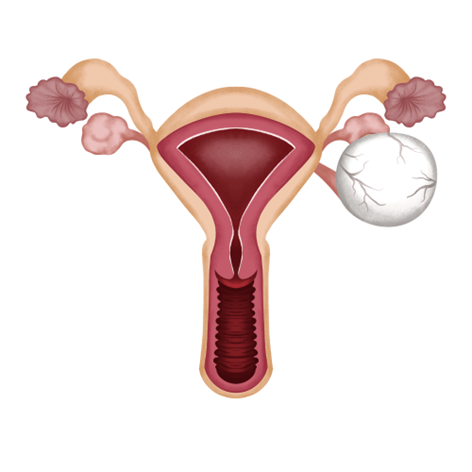
Ovarian cysts are common growths that form either inside or on the surface of the ovaries. These cysts typically contain fluid or semi-solid material and can vary in type. Most ovarian cysts are harmless, often asymptomatic, and tend to resolve without treatment. However, in some cases, they may cause complications that require medical attention, making regular pelvic examinations essential for early detection and management.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
Most ovarian cysts are classified as functional cysts, which develop due to the normal processes of the menstrual cycle. These cysts generally resolve on their own within a few months.
Non-functional cysts, such as cystadenomas, dermoid cysts, endometriomas, and ovarian cancerous tumors, can present more significant health concerns and require closer monitoring or intervention.
Symptoms and Causes
Ovarian cysts are most commonly caused by ovulation, but other factors such as abnormal cell growth, endometriosis, and pelvic inflammatory disease contribute to their development. Symptoms vary based on the size and type of cyst. Smaller cysts often go unnoticed, while larger cysts may cause pelvic pain, bloating, discomfort during intercourse, or irregular menstrual cycles.
Diagnosis and Testing
Ovarian cysts are usually diagnosed through pelvic examinations and imaging tests, such as ultrasounds or laparoscopy. These diagnostic tools help determine the size, location, and type of cyst, which informs the best treatment plan.
Management and Treatment
Treatment options depend on factors such as the patient's age, symptoms, and the type of cyst. Functional cysts may only require watchful waiting, while larger or symptomatic cysts may need surgical intervention. Hormonal medications may also be prescribed to regulate ovulation and prevent new cysts from forming.
Prevention
Hormonal contraceptives may reduce their recurrence. Regular pelvic exams and prompt attention to any symptoms aid in early detection and treatment.
Living With Ovarian Cysts
Those with ovarian cysts should monitor their symptoms and follow their doctor's guidance for follow-up care. For women with endometriotic cysts or those requiring surgery, fertility may be affected, so it may be advisable to freeze eggs before undergoing surgery. Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers ensures timely intervention and better overall health outcomes.